 GEOSPATIAL TOOL
GEOSPATIAL TOOL
MedBioLitter
TO WHOM IS ADDRESSED?
Conservationists, funding programmes, Marine Protected Area (MPA) managers, public authorities, researchersTHEME
Marine litterKEYWORDS
Biodiversity, ecosystem approach, environmental data, marine litter, Marine Protected Area, Mediterranean, policy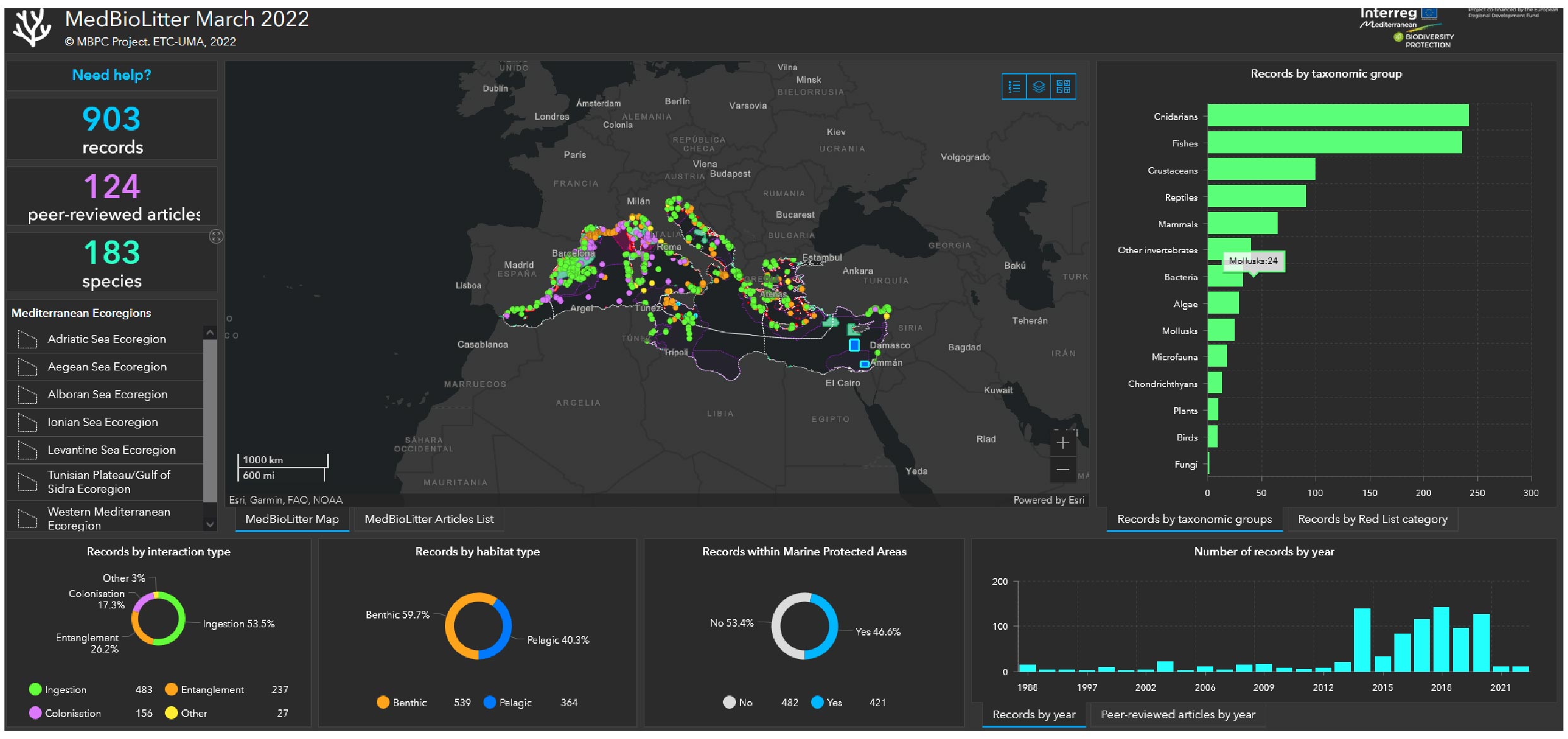

WHAT PROBLEM WOULD THIS SOLVE?
Research efforts are increasing our knowledge on the amount, composition and impacts of marine litter on marine ecosystems, biodiversity and people. However, the number of studies is scattered and geographically unbalanced, making it difficult for policy makers, managers, the business sector and the general public to accurately understand the dimensions of such a modern challenge and the urgent need to react.
Aim of the tool
The aim of MedBioLitter is to support scientists, decision makers and managers in providing a structured and visual overview of the scientific knowledge necessary to tackle the issue of marine litter and its negative impacts on biodiversity in the Mediterranean.
Main objectives
The objective of MedBioLitter’s open database and spatial geoportal, including an interactive viewer providing access to statistical information, is to provide a searchable one entry-point to peer reviewed research evidence published on the impacts of marine litter on marine biota in the Mediterranean region.

WHAT IS NEEDED FOR IMPLEMENTATION?
Technological infrastructure
A PC, tablet or smartphone, an internet browser and an internet connection are required to access the MedBioLitter Platform.
Training
No particular training is necessary to access and use the Platform, only basic knowledge as an Internet user.
Investment
The access and use of the platform is free-of-charge.

HOW TO USE IT?
Concept
The MedBioLitter database includes the geolocation of more than 900 interaction records across several areas studied and for more than 180 species, as well as providing direct access to more than 100 peer-reviewed articles. Parameters referring to the geographical location of the interactions, relevant policies and directives, ongoing protection frameworks (including reference to the IUCN Red List), species assessed, their habitats and conservation status, and the interaction with marine litter registered per marine compartment (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), are available in MedBioLitter. Each MedBioLitter spatial registry of an interaction directs the user to the reference source and the authors of the peer reviewed article published. Furthermore, the database includes a mechanism for any author interested to submit new information for analysis and inclusion in future updates.
Pilot areas
This tool has been built to cover the whole Mediterranean, and as such has not been piloted in any specific area.
Implementation Dates
Hosted by ETC-UMA, the MedBioLitter thematic database is updated every 6 months during March and September each year. Updates include the identification and selection of new entries for the Mediterranean Sea as included in LITTERBASE and additional searches and studies of peer reviewed publications.

WHAT CHALLENGES MAY ARISE?
As for other similar geoportals, the quality and accuracy of the search results and of the records, depends on the quality and standardisation of the data input. Moreover, it may not be immediately usable to all users, especially those that are not experts or trained in using geoportals. To address this, a dedicated help page has been developed to teach the user how to navigate the interactive viewer and find the data of their interest.

WHAT ARE THE EXPECTED RESULTS?
Quantitative results
The result of using MedBioLitter is an increase in the knowledge of decision makers, scientists and managers of the interactions and impacts of marine litter on biodiversity in specific areas of the Mediterranean, in order to support the design and implementation of effective policies and management strategies to minimise such impacts. The Mediterranean data dashboard interactive viewer developed in 2021 provides statistical information as a digest and foundation for further analysis.
Key deliverables
Regular summary of the results in factsheets and policy reports, published on the MBKP.
Transfer potential
MedBioLitter is an open and continuously growing database. It is a useful tool addressed to all scientists, decision makers and managers throughout the Mediterranean that are interested in the themes of marine litter and interactions with biodiversity. It has already supported relevant studies on the impacts of marine litter on biodiversity. Further connections may be developed to ensure a wider spatial, temporal and thematic coverage of the data.
KEY INFORMATION
- Individuals and institutions interested in adding their peer-reviewed results can send their manuscripts or publications to the MedBiolitter team for consideration and integration in the database. A contact form is available online from the Mediterranean Biodiversity Protection Knowledge Platform (biodiversity.uma.es). Authors interested in providing their data and research outcomes can also do so following the required parameters and format by uploading their data through the “submit data” button on the Mediterranean Biodiversity Protection Knowledge Platform.
- Waters belonging to the countries of the European Union present more than 90% of the data. This highlights the need to strengthen data collection and the monitoring of marine litter and its interactions with biodiversity in the Southern part of the Mediterranean, where information is largely lacking.
For further information
Project name:
- Mediterranean Biodiversity Protection Community (MBPC)
- ENSERES – ENhancing Socio-Ecological RESilience in Mediterranean coastal areas
Project Contact: ETC-UMA
- Project Contact : Antonio Sánchez, ETC-UMA (a_sanchez@uma.es)
Links of interest:
- MedBioLitter
- MedBioLitter Help page
- Report on Marine mega fauna and litter in the Mediterranean. An overview of impacts in MedBioLitter – April 2022
- Report on Mapping the State of Knowledge on Marine Litter and Biodiversity Interactions in the Mediterranean Sea – December 2019
Partners:
- Adriatic Ionian Euroregion (AIE)
- American University of Beirut- FAFS
- Arab Network for Environment and Development (RAED)
- CPMR-Conference of Peripheral Maritime Regions of Europe
- European Topic Centre – University of Malaga
- Goverment of Catalonia, Directorate General of Fisheries and Maritime Affairs
- IUCN World Commission on Protected Areas (IUCN-WCPA )
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) – Centre for Mediterranean Cooperation
- Italian National Institute for Environmental Protection and Research (ISPRA)
- Latin Arco – Arc Latin
- Latte Creative
- Legambiente
- Marine Institute
- Medcities
- Mediterranean Protected Areas Network – MedPAN
- Ministry of Sustainable Development and Tourism (MSDT)
- Municipality Herceg Novi
- Plan Bleu – Regional Activity Centre (PB/RAC)
- Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur Region PACA
- Public agency for promotion of entrepreneurship and developing projects of Municipality of Izola
- Region of Crete
- Regional Activity Centre for Specially Protected Areas – RAC/SPA
- Regione Lazio
- Service de protection de la nature et politiques des forêts de la Région Autonome de Sardaigne
- Small Islands Organisation – SMILO
- The Resource Environmental Center (REC)
- Tour du Valat Foundation
- University of Balamand
- Ville de Marseille
- WWF Mediterranean
Project

Donor






